Molluscum contagiosum is a relatively common viral skin infection, primarily in childhood, that produces localized clusters of papules or raised bumps on the skin’s upper layers. These small bumps are usually painless, and they resolve without treatment, typically within 2 months to 4 years. However, for certain individuals, such as those with a weakened immune system, this virus can be more difficult to treat and cause more severe effects. For severe molluscum contagiosum, medication and surgical treatments may be required. Here, our Gainesville dermatology specialists discuss everything you need about molluscum contagiosum and possible treatment options.
Our dermatologists in Gainesville are dedicated to providing the high-quality care possible within our full-service dermatology practice. Contact Dermatology Associates today to schedule an appointment!
What Is Molluscum Contagiosum?
Molluscum contagiosum, also known as water warts or poxvirus, is a fairly common viral infection of the skin, creating round, firm, and painless bumps from the size of a pinhead to the eraser of a pencil. The infection can spread to the surrounding skin if the bumps are scratched or sustain an injury. This skin condition can also spread through person-to-person contact and contact with objects infected with the virus. Molluscum contagiosum most commonly occurs in children, though adults can also become infected. In adults with otherwise normal immune systems, molluscum contagiosum affecting the genitals is considered a sexually transmitted disease (molluscum contagiosum STD).
Molluscum Contagiosum Symptoms
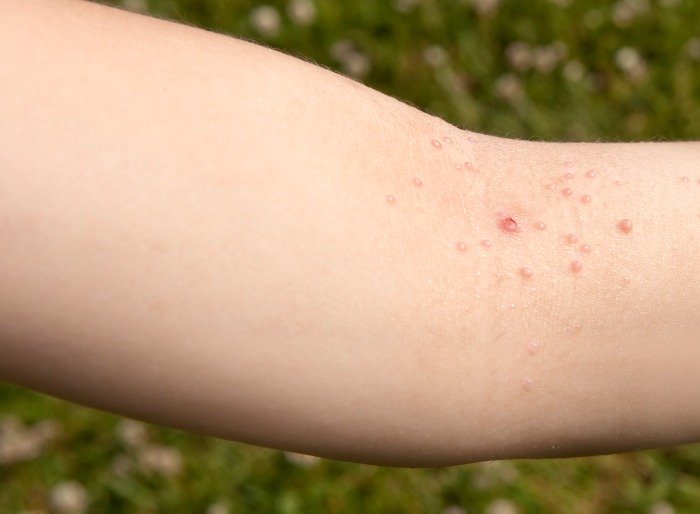
The typical signs and symptoms of molluscum contagiosum include raised, round, and flesh-colored bumps on the skin, which are usually small in size, measuring less than a quarter-inch around, or smaller than 6 millimeters. These bumps characteristically feature a tiny indentation or a dot at the center of each bump, which can become red and inflamed and may be itchy or cause discomfort.
These bumps can be easily removed when scratched or rubbed, but breaking open these lesions can quickly spread the virus to the surrounding skin. The bumps generally appear on the face, neck, armpits, and the tops of the hands in children. In adults, they may also be seen on the genitals, lower stomach, and inner upper thighs if the infection is sexually transmitted.
Molluscum Contagiosum Stages
The first signs and symptoms of beginning molluscum contagiosum are the development of small, painless papules, or raised bumps or lumps, on the skin, commonly referred to as molluscum lesions. These lesions appear as raised, pearl-pink, or pearl-like nodules or redness on the skin. Often, these bumps contain a dimple at their center, and most are small. Within the bump, there may be a whitish, pus-like core. The bumps can become itchy when scratched, and they may also develop redness and inflammation and can appear anywhere on the body. There are typically three stages to this skin condition.
The molluscum contagiosum early stages are characterized by small, white, or red bumps on the skin. Over a few weeks, the bumps can enlarge and develop a white-colored pus head that creates a small crater when it bursts. Our dermatologists advise patients against attempting to intentionally pop the bumps to prevent molluscum contagiosum getting worse and spreading to other areas of the body. During the molluscum contagiosum final stages, the burst crater lesions develop into red-colored sores. At this stage, secondary infections can infect the open sores.
How Do You Get Molluscum Contagiosum?
With part of this skin condition’s name being “contagiosum,” you can be sure molluscum contagiosum is contagious. The virus that causes molluscum contagiosum can spread via direct, skin-to-skin contact and indirect contact. With indirect contact, towels or personal items used in contact sports previously touched by a person infected with molluscum contagiosum allow the virus to pass from the personal item to another person’s skin.
Additionally, scratching molluscum contagiosum sores or touching other parts of the body with the infected skin can cause the infection to spread to the infected person’s surrounding, healthy skin. The molluscum contagiosum virus can also be spread to other parts of the body through shaving and electrolysis or from one person to another through sexual contact. Once transmitted, the molluscum contagiosum virus remains in the top layer of skin and does not circulate throughout the body.
As such, it cannot spread through coughing and sneezing. Because the virus lives in the epidermis, once the lesions disappear, the virus is gone, and you cannot spread it to others. You may develop pink eye if molluscum contagiosum lesions appear on the eyelids.
How To Treat Molluscum Contagiosum
If you or your child have molluscum contagiosum, seeing a dermatologist can offer you multiple benefits. Your dermatologist will be able to diagnose your skin condition and determine whether it is molluscum contagiosum or something else. A number of skin conditions can look similar to molluscum contagiosum, especially to the untrained eye. If you are diagnosed with molluscum contagiosum, your dermatologist can inform you whether or not treatment is necessary and discuss your treatment options. In most cases, your dermatologist can usually diagnose molluscum contagiosum just by looking at the bumps on your skin.
They may scrape off a small portion of the infected skin and test it under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis. Your dermatologist may recommend clearing the infection, particularly if you have a healthy immune system. However, in other situations, molluscum contagiosum treatment may be necessary. Treatment may be recommended for those with a chronic skin condition, such as eczema, those with the infection in their genital area, those with a weakened immune system and multiple lesions, and those with molluscum contagiosum that produces bothersome side effects and symptoms.
Your doctor will discuss the best treatment option with you during your appointment. A molluscum contagiosum treatment cream, a medical wart remover for molluscum contagiosum, cantharidine solution, and antiseptics may be recommended to help clear up the infection. Other treatments, such as cryotherapy, gentle curettage, or laser therapy, may be available. Contact Dermatology Associates today to discuss your treatment options.
How Long Does Molluscum Contagiosum Last?
In people with a healthy immune system, molluscum contagiosum usually resolves without treatment, though some individuals may require treatment from their dermatologist. Without treatment, the infection typically disappears gradually, within a year or more, without leaving scars. Though for some individuals, it may take a few months to several years for their molluscum contagiosum to clear. The infection can last even longer and prove more persistent in those with a compromised immune system. Once the lesions disappear, the virus is no longer present in the body, and it cannot be spread to others or to other parts of your body. If you have had molluscum contagiosum once, it is possible to become infected again.
How To Prevent Molluscum Contagiosum
The best way to avoid contracting molluscum contagiosum and transmitting the virus to others is to avoid touching another person’s skin with the infection. Following these recommendations can also help you prevent the spread of infection.
- Wash your hands regularly with warm water and antibacterial soap
- Instruct children in proper handwashing techniques
- Avoid sharing any personal items, including clothing, towels, hairbrushes, and bar soap
- Don’t use shared sports equipment that has come into contact with another person’s bare skin
- Do not pick at, touch, or scratch areas of your skin where molluscum contagiosum bumps are visible
- Maintain cleanliness around the bumps and keep them covered to avoid infecting another area of your skin and transferring it to others
- Avoid shaving and using electrolysis in the affected areas of skin
- Avoid sexual contact if you have molluscum contagiosum bumps in your genital area